Holographic Symphonies: The Future of Orchestral Performance
In a world where technology and artistry increasingly intertwine, a groundbreaking fusion of classical music and cutting-edge holography is reshaping the landscape of orchestral performances. This innovative approach, known as holographic symphonies, is captivating audiences worldwide and challenging traditional notions of live music experiences. As holographic technology advances, orchestras are exploring new dimensions of creativity, bringing long-gone composers back to the conductor's podium and transporting audiences to fantastical realms. This article delves into the fascinating world of holographic symphonies, examining their impact on the classical music scene and the potential they hold for the future of artistic expression.
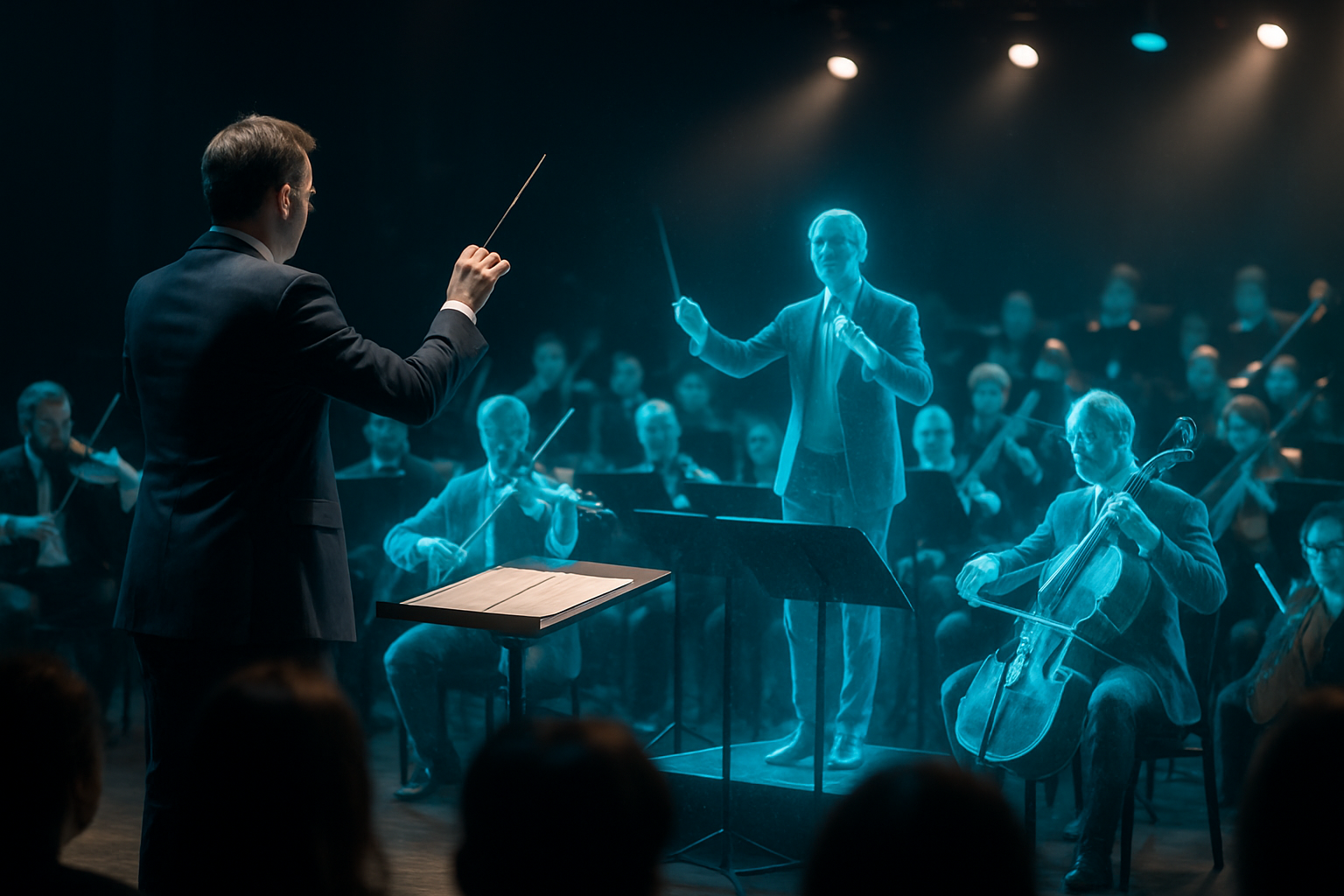

Technological Marvels Behind the Music
At the heart of holographic symphonies lies a complex array of cutting-edge technologies. High-powered laser projectors, advanced motion capture systems, and sophisticated computer algorithms work in harmony to create lifelike, three-dimensional images that appear to occupy physical space alongside the musicians. These holograms are not mere pre-recorded videos; they are responsive, adapting to the nuances of each live performance and creating a truly immersive experience for both the audience and the performers.
Reimagining Classical Compositions
One of the most exciting aspects of holographic symphonies is the ability to breathe new life into classical compositions. Imagine watching a holographic Johann Sebastian Bach conduct his own Brandenburg Concertos or seeing Ludwig van Beethoven’s emotions come to life as his Ninth Symphony unfolds. These virtual resurrections of legendary composers offer audiences a unique connection to the music’s historical context and the creator’s original vision, bridging centuries of musical evolution in a single performance.
Creating New Worlds of Sound and Vision
Beyond historical recreations, holographic symphonies open up entirely new avenues for artistic expression. Composers and visual artists collaborate to create fantastical landscapes that evolve in sync with the music, transporting audiences to otherworldly realms. From abstract geometric patterns that pulse with the rhythm to fully realized virtual environments that tell stories alongside the musical narrative, these performances blur the lines between concert and immersive art installation.
The Impact on Audience Engagement
Holographic symphonies are revolutionizing the way audiences engage with classical music. Traditional barriers to appreciation, such as the perceived stuffiness of concert halls or the challenge of visualizing abstract musical concepts, are being dismantled. Young audiences, raised on a diet of high-tech entertainment, find themselves drawn to these multisensory experiences, while seasoned classical music lovers discover new depths in familiar pieces. The result is a broadening and diversification of the classical music audience, breathing new life into an art form often considered niche or elitist.
Challenges and Controversies
As with any revolutionary art form, holographic symphonies face their share of challenges and criticisms. Purists argue that the visual spectacle detracts from the purity of the musical experience, while others raise concerns about the authenticity of performances featuring holographic historical figures. Technical challenges, such as the need for specialized venues and the high cost of production, also present obstacles to widespread adoption. Additionally, questions of copyright and ethical considerations surrounding the digital resurrection of deceased artists continue to spark debate within the musical and legal communities.
The Future of Holographic Symphonies
Despite the challenges, the future of holographic symphonies looks bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more realistic and interactive holographic elements, potentially allowing audience members to influence the visual aspects of the performance in real-time. The boundaries between virtual and physical realities may blur further, with augmented reality technologies enabling personalized holographic experiences for each audience member. Moreover, the potential for remote holographic performances could democratize access to world-class orchestras, bringing these immersive experiences to audiences around the globe.
In conclusion, holographic symphonies represent a bold step forward in the evolution of classical music performance. By marrying centuries-old musical traditions with cutting-edge technology, this innovative art form is attracting new audiences, inspiring fresh creativity, and ensuring that the timeless beauty of orchestral music remains relevant in our rapidly changing world. As we look to the future, it’s clear that holographic symphonies are not just a passing trend, but a transformative force that will continue to shape the landscape of musical performance for years to come.